Code overview
Conda environment setup
All of the required dependencies can be installed as a conda environment using
the environment.yaml file in the repository. More instructions can be found
in the README
file.
Startup scripts
The X series devices require some initial network configuration. For convenience, a startup script is provided to automate this setup. You may need to tweak this file to your setup.
Runner scripts
The basic steps required to run the radar are:
- Build the C++ code
- Generate a chirp file to transmit based on your configuration
- Run the compiled radar code
- Move the collected data to an appropriate location
The main interface for running the radar code is through run.py, a Python
script designed to automate the above process. This script is run as follows:
python run.py config/my_radar_configuration.yaml
At the end of the data collection, data will be saved with the current date to a location specified in the YAML config file.
Generally, three files are saved:
YYYYMMDD_hhmmss_rx_samps.bin- This is a binary file containing the raw samples recorded the SDR. Note that this file is not interpretable unless you also have the config file used.YYYYMMDD_hhmmss_config.yaml- This is the YAML config file passed torun.py. It defines all parameters of the data collection, allowing for therx_samps.binfile to be interpreted and processed.YYYYMMDD_hhmmss_uhd_stdout.log- This is a text file containing the output of running the radar code. This is helpful for debugging and also contains a log of any errors encountered, which may be required to reconstruct the timing of each recording.
More details on the files stored and how these can be re-processed into a Zarr file are on the file formats page.
Note that there are also settings available to break rx_samps.bin into multiple
files as needed.
SDR interface code
For performance reasons, the code directly interfacing with the SDR is written
in C++. This code is all located in the sdr/ directory of the repository.
The main radar code is contained in main.cpp (with some SDR setup code located
in rf_settings.cpp). The radar code runs in two threads, as shown in the
figure below.
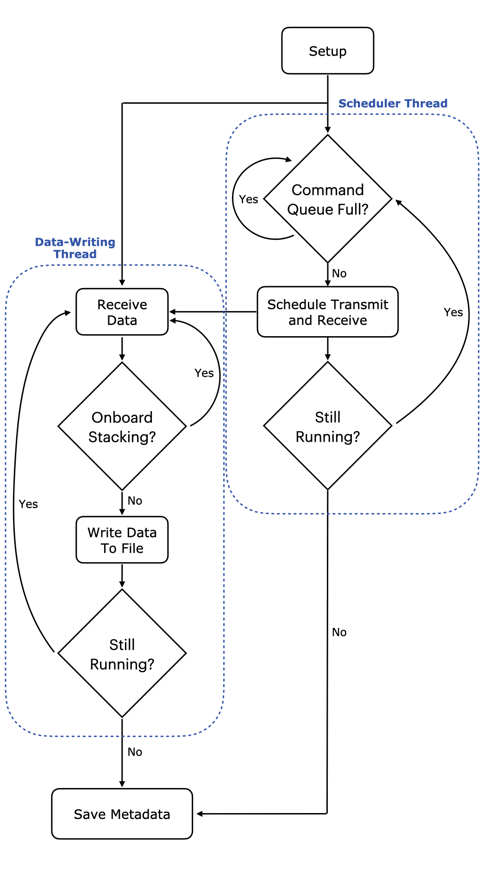
General architecture of the ORCA code
One thread is responsible for scheduling timed commands that are enqueued into FIFO queues within the SDR’s FPGA.
The other thead is responsible for pulling received samples from the SDR and writing them to a file on the host computer.
For a more complete overview, please refer to our paper:
T. O. Teisberg, A. L. Broome and D. M. Schroeder, “Open Radar Code Architecture (ORCA): A Platform for Software-Defined Coherent Chirped Radar Systems,” in IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 62, pp. 1-11, 2024, Art no. 5109411, doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3446368.